A recent archaeological excavation at Gullberg Fortress in Sweden has uncovered a fascinating array of artefacts, including a distinctive dagger known as a ‘bollock dagger’ or a ‘ballock dagger’. The findings shed light on medieval life and offer a glimpse into the fortress’s history as a strategic stronghold. Located in Västra Götaland, the 13th-century fortress has revealed these objects during ongoing digs by the University of Gothenburg, sparking interest in their historical and cultural significance. The excavation in spring 2025 unearthed several well-preserved items buried in the fortress’s soil. Among them is a bronze dagger, approximately 20 centimetres long, with…
-
-
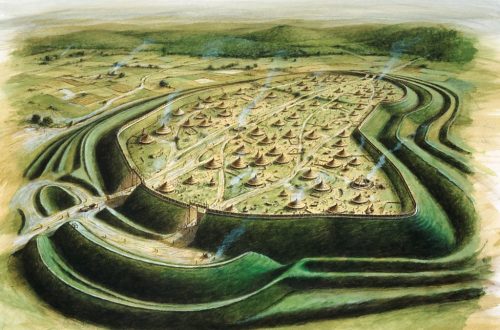
Recent archaeological discoveries off the coast of Scotland have illuminated the remarkable journeys of prehistoric peoples who ventured to the far northern reaches of the British Isles around 10,000 years ago. Submerged stone tools and possible structural remains found near the Isle of Skye suggest that early humans, likely Mesolithic hunter-gatherers, braved challenging conditions to settle in regions previously thought to be sparsely populated. This finding, reported by the University of Glasgow, challenges assumptions about the extent of prehistoric human migration and highlights the resilience of our ancestors. Archaeologists from the University of Glasgow, led by Professor Karen Hardy, have…
-
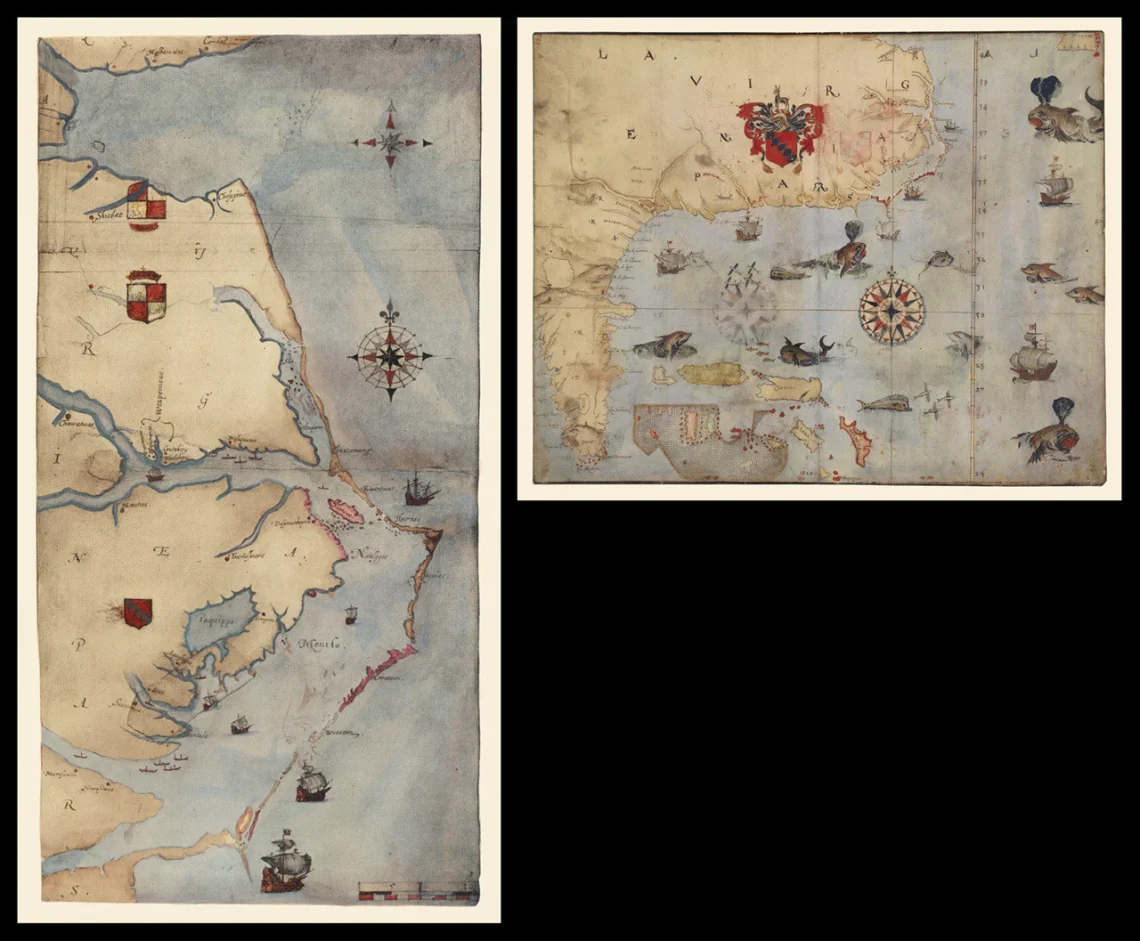
For over four centuries, the fate of the Lost Colony of Roanoke has remained one of America’s most enduring historical enigmas. In 1587, over 100 English settlers, led by Governor John White, established a colony on Roanoke Island, off the coast of present-day North Carolina. When White returned in 1590 after a three-year delay due to the Anglo-Spanish War, the colony was deserted, with only the word “CROATOAN” carved into a wooden post as a clue. Now, groundbreaking archaeological discoveries on Hatteras Island have provided compelling evidence that the colonists did not vanish but integrated with the local Croatoan tribe,…
-
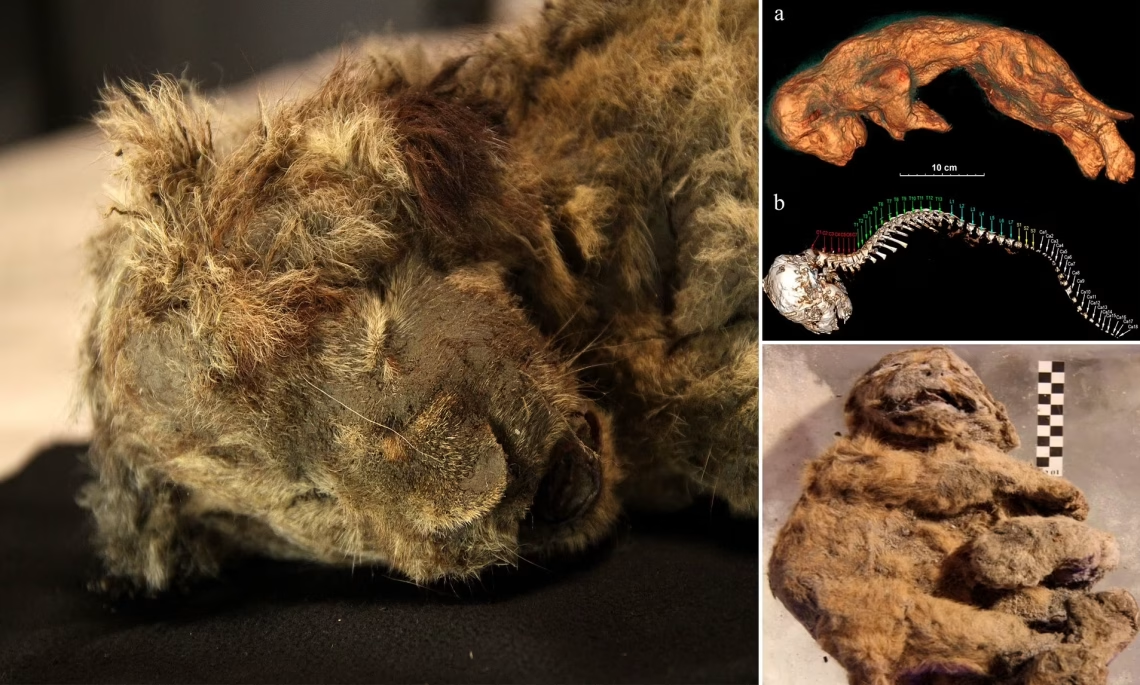
In Siberia’s permafrost, mammoth tusk collectors uncovered two remarkably preserved cave lion cubs, Boris and Sparta, in 2017 and 2018. These cubs, aged one to two months when they died roughly 28,000 and 43,000 years ago, offer a rare glimpse into the Ice Age. With fur, whiskers, and even traces of mother’s milk preserved, they rank among the best-preserved Ice Age animals ever discovered. The collectors spotted the cubs along the Semyuelyakh River in Russia’s Yakutia region, buried 10 to 12 meters deep. The female, Sparta stands out for her near-perfect condition, with intact claws and fur, while Boris provides…
-
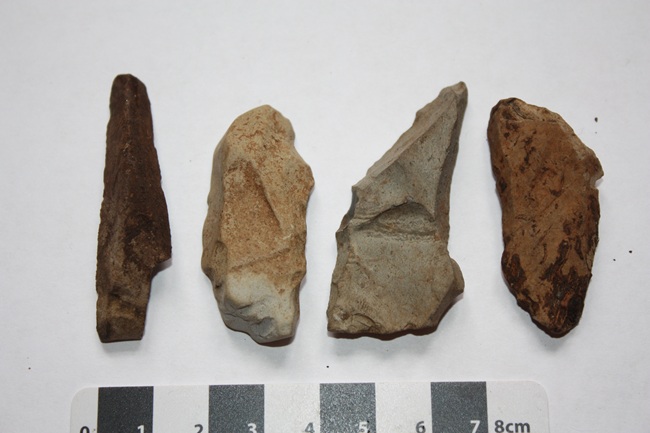
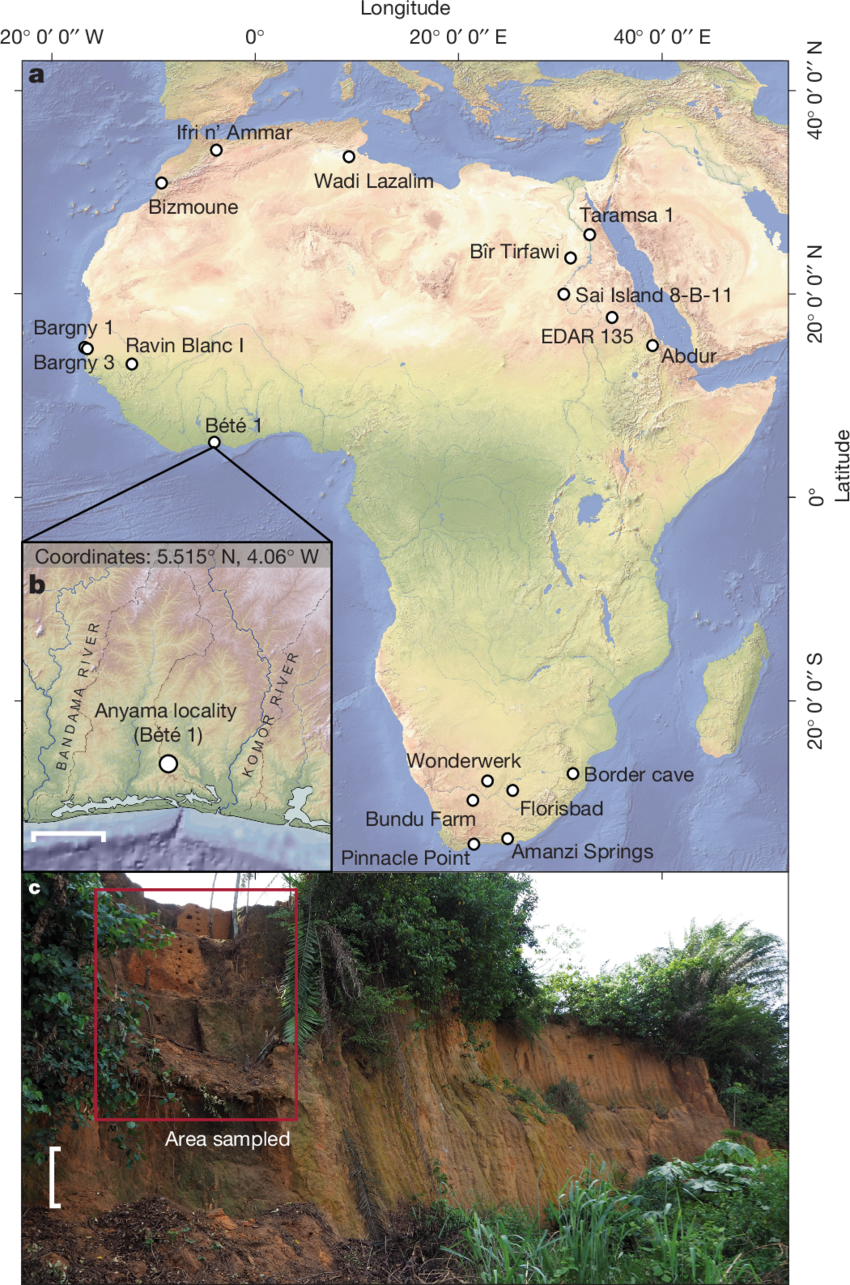
A remarkable archaeological find in West Africa has unveiled evidence that early humans inhabited tropical rainforests as far back as 150,000 years ago, challenging long-held assumptions about the environments our ancestors occupied. The discovery, centered at the Bété I site in southern Côte d’Ivoire, marks the earliest known association between humans and wet tropical forests, pushing back the timeline of rainforest habitation in Africa by over 130,000 years. The Bété I site, first explored in the 1980s by a joint Ivorian-Soviet team, yielded stone tools such as picks and retouched flakes buried in layers of sediment. Initially, limitations in dating…
-
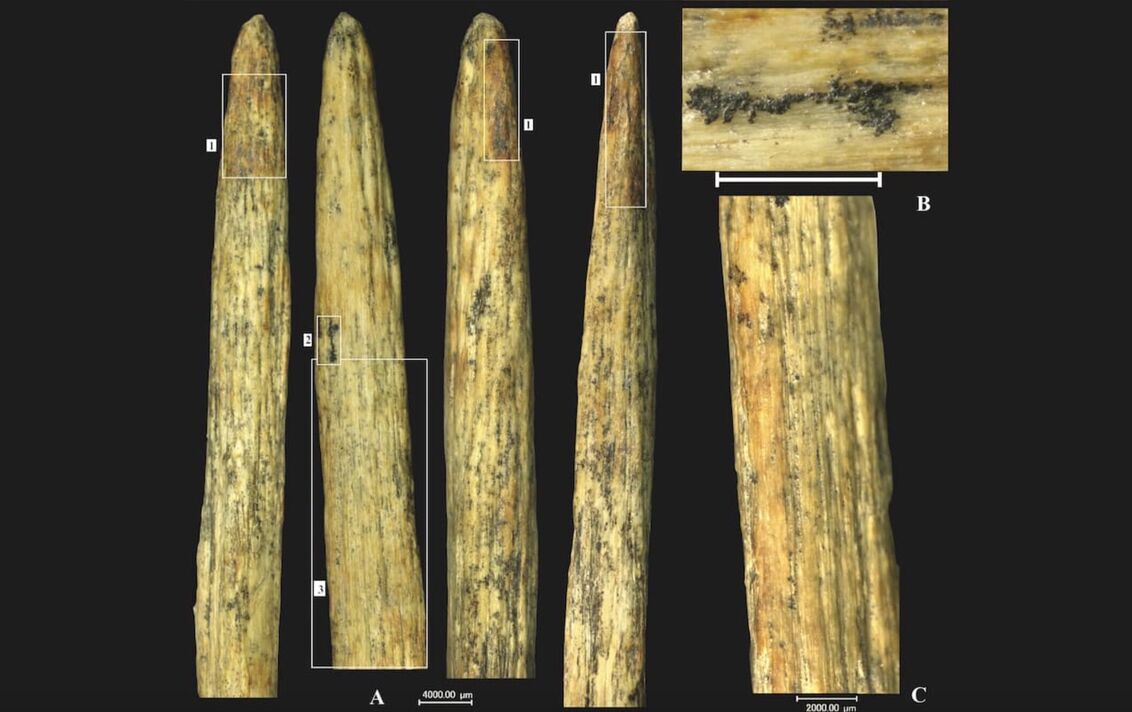
A remarkable discovery in northern Spain has uncovered what is believed to be Europe’s oldest bone spear point, dated to approximately 52,000–54,000 years ago. Found at the Abric Pizarro rock shelter in the Pyrenees, this artefact highlights the advanced tool-making skills of Neanderthals, offering fresh insights into their technological capabilities. An international team of archaeologists unearthed a finely crafted spear point made from a horse’s long bone during excavations at Abric Pizarro. Analysed using advanced radiocarbon dating, the artefact is estimated to be 52,000–54,000 years old, making it older than other known bone tools in Europe, such as those found…
-
Today, May 8, 2025, the National Trust’s Sutton Hoo unveils a captivating new exhibition, The Dig: A Story Unearthed, which delves into the real-life events and personalities that inspired the acclaimed Netflix film The Dig. This exhibition, set at the iconic Anglo-Saxon burial site in Suffolk, offers archaeology enthusiasts and history lovers a chance to explore the remarkable story of the 1939 excavation that reshaped our understanding of early medieval England. The exhibition centres on the discovery of the Great Ship Burial in Mound 1, a find that revealed a 27-meter-long ship and a treasure trove of Anglo-Saxon artefacts, including…
-
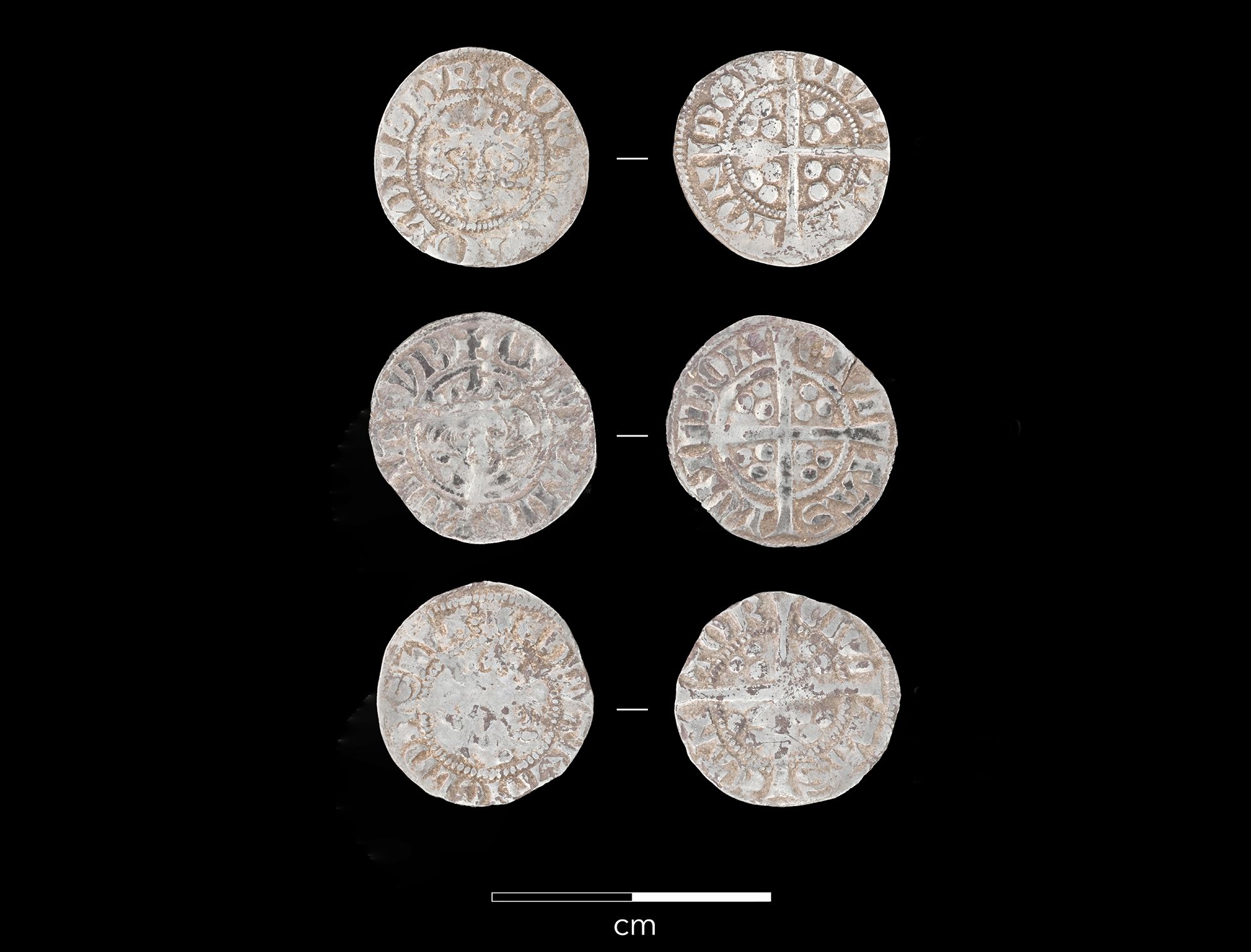
Three unassuming silver pennies, unearthed together in Essex, offer a poignant glimpse into the lives and potential misfortunes of early 14th-century England. Struck during the reigns of Edward I and his son, Edward II, the close dating of these coins suggests they were lost as a small hoard, perhaps the contents of a dropped purse. The most recent penny dates to between 1314 and 1317, placing their loss firmly in the early decades of a century marked by widespread hardship. Intriguingly, this precise period aligns with the devastating livestock and agricultural disasters that gripped England. Higher than average rainfall and…
-
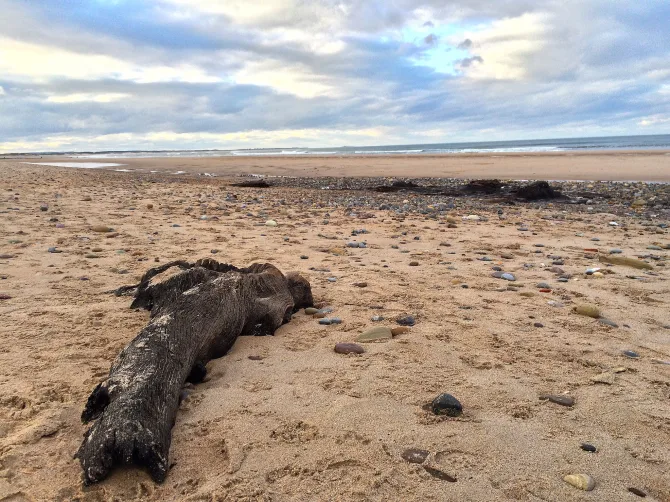
Doggerland, once a thriving prehistoric landscape, now lies submerged beneath the North Sea, connecting Britain to continental Europe. Occasionally exposed by winter storms, the remains of this ancient submerged forest, part of the Mesolithic landscape of Doggerland, emerge from the sands of Cresswell Beach. The remains at Cresswell Beach include stumps and felled trunks of Oak, Hazel and Alder trees, preserved by peat deposits. These remnants date back over 7,000 years, thriving during the Mesolithic period. This forest existed before Britain’s separation from continental Europe, a result of rising post-glacial sea levels that transformed the region into what is now…
-
2,300-year-old Celtic sword from France Discovered A 2,300-year-old Celtic sword from France is been discovered and is a striking find. Discovered in 2022 at Creuzier-le-Neuf, this Iron Age relic, adorned with swastika motifs, reveals the skilled metalwork of ancient Celts. A Spectacular Burial Find Archaeologists from the French National Institute of Preventive Archaeological Research (INRAP) excavated a Second Iron Age necropolis (450–52 BCE) in central France, uncovering over 100 graves. Acidic soil dissolved skeletons, but metal artefacts endured, including copper-alloy bracelets, iron brooches, and two swords in their scabbards. The standout is a short sword, its copper-alloy sheath gleaming with…