A recent archaeological excavation in Chichester’s Priory Park has revealed the remains of a stone tower, known as a barbican, which once defended the city’s Norman castle. The discovery, made during a two-week dig led by Chichester District Council’s archaeologist James Kenny in collaboration with the Chichester and District Archaeological Society (CDAS), sheds new light on the city’s 11th-century history. The excavation, which concluded in early June 2025, focused on an area north of The Guildhall in Priory Park. Guided by geophysics and ground-penetrating radar scans conducted since 2022, the team uncovered the remains of a substantial stone structure measuring…
-
-
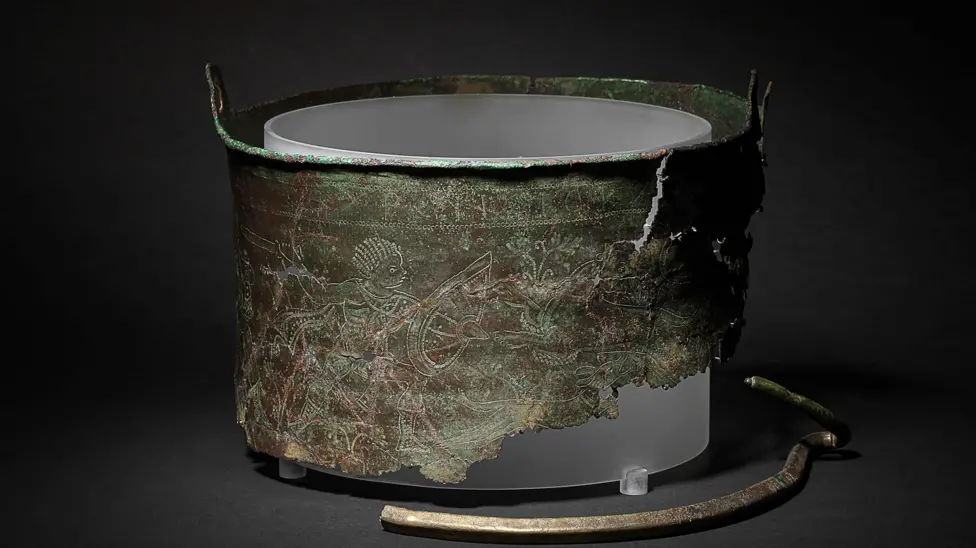
Archaeologists have confirmed that a 6th-century Byzantine bucket discovered at Sutton Hoo, Suffolk, likely served as a cremation vessel. The bucket, pieced together from fragments found over decades, contained cremated human and animal bones, offering new insights into burial practices of the early medieval period in England. The bucket’s fragments were first unearthed in 1986, with additional pieces discovered in 2012 and 2024 during excavations at the site. Located near Woodbridge, Sutton Hoo is renowned for its Anglo-Saxon burial mounds, including the famous ship burial of 1939, believed to be the resting place of King Raedwald of East Anglia, who…
-
Archaeologists in Varberg, Sweden, have discovered six historical shipwrecks during investigations for the Varbergstunneln project. The finds, located near the original shoreline in southwest Sweden, range in age from the Middle Ages to the 17th century, offering new insights into the region’s maritime history. The discoveries were made by teams from the Bohuslän Museum, Visual Archaeology, and Cultural Environment Halland, as part of preparatory work for the tunnel construction. The shipwrecks were found in an area historically significant for maritime activity, close to Varberg’s coastline. The vessels vary in age, with some dating back to the medieval period, providing a…
-
A recent archaeological excavation at Gullberg Fortress in Sweden has uncovered a fascinating array of artefacts, including a distinctive dagger known as a ‘bollock dagger’ or a ‘ballock dagger’. The findings shed light on medieval life and offer a glimpse into the fortress’s history as a strategic stronghold. Located in Västra Götaland, the 13th-century fortress has revealed these objects during ongoing digs by the University of Gothenburg, sparking interest in their historical and cultural significance. The excavation in spring 2025 unearthed several well-preserved items buried in the fortress’s soil. Among them is a bronze dagger, approximately 20 centimetres long, with…
-
In a remarkable find, researchers at Cambridge University Library have discovered fragments of a rare 13th-century manuscript containing medieval tales of Merlin and King Arthur. Hidden for centuries within the binding of a 16th-century ledger, these parchment fragments offer a fresh glimpse into the Arthurian legend, shedding light on its medieval French origins. Digitised through a groundbreaking three-year project, the manuscript is now accessible to scholars and the public, marking a significant moment in literary and historical research. The manuscript fragments were found by an archivist examining the binding of a 16th-century estate register. The parchment, dating to around 1300,…
-
Today, May 8, 2025, the National Trust’s Sutton Hoo unveils a captivating new exhibition, The Dig: A Story Unearthed, which delves into the real-life events and personalities that inspired the acclaimed Netflix film The Dig. This exhibition, set at the iconic Anglo-Saxon burial site in Suffolk, offers archaeology enthusiasts and history lovers a chance to explore the remarkable story of the 1939 excavation that reshaped our understanding of early medieval England. The exhibition centres on the discovery of the Great Ship Burial in Mound 1, a find that revealed a 27-meter-long ship and a treasure trove of Anglo-Saxon artefacts, including…